2025
|
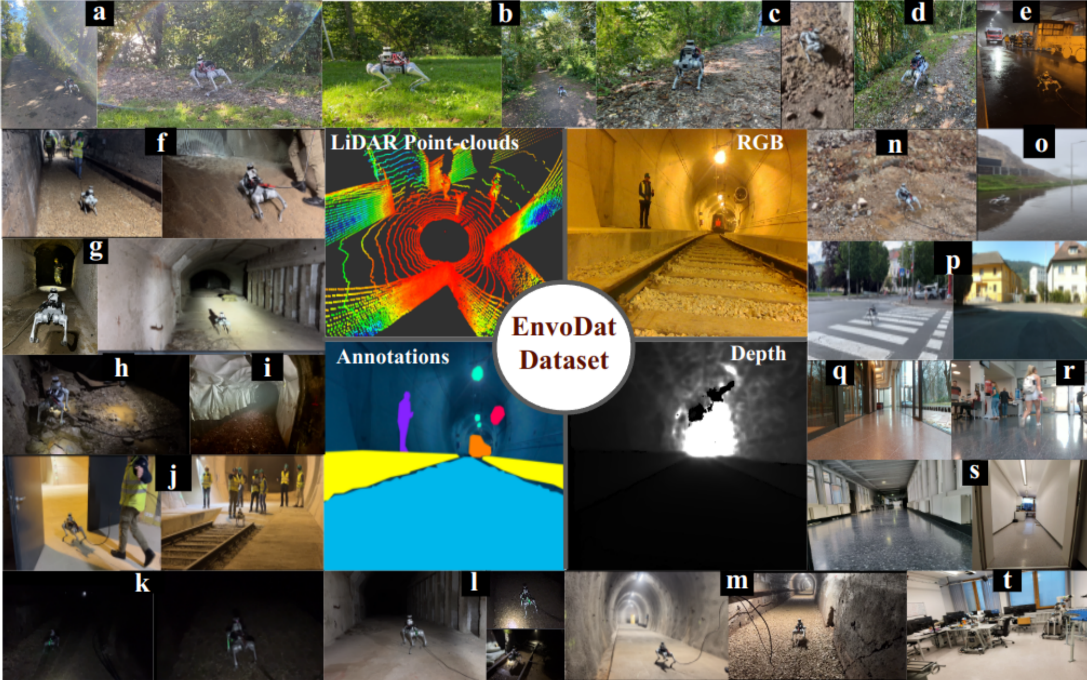
Nwankwo, Linus; Ellensohn, Bjoern; Dave, Vedant; Hofer, Peter; Forstner, Jan; Villneuve, Marlene; Galler, Robert; Rueckert, Elmar EnvoDat: A Large-Scale Multisensory Dataset for Robotic Spatial Awareness and Semantic Reasoning in Heterogeneous Environments Proceedings Article In: IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA 2025)., 2025. @inproceedings{Nwankwo2025,
title = {EnvoDat: A Large-Scale Multisensory Dataset for Robotic Spatial Awareness and Semantic Reasoning in Heterogeneous Environments},
author = {Linus Nwankwo and Bjoern Ellensohn and Vedant Dave and Peter Hofer and Jan Forstner and Marlene Villneuve and Robert Galler and Elmar Rueckert},
url = {https://cloud.cps.unileoben.ac.at/index.php/s/MawgtYSbTBoNBZo},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-01-27},
urldate = {2025-01-27},
booktitle = {IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA 2025).},
keywords = {Autonomous Navigation, robotics, SLAM},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
|  |
2023
|
Nwankwo, Linus; Rueckert, Elmar Understanding why SLAM algorithms fail in modern indoor environments Proceedings Article In: International Conference on Robotics in Alpe-Adria-Danube Region (RAAD). , pp. 186 - 194, Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland., 2023. @inproceedings{Nwankwo2023,
title = {Understanding why SLAM algorithms fail in modern indoor environments},
author = {Linus Nwankwo and Elmar Rueckert},
url = {https://cloud.cps.unileoben.ac.at/index.php/s/KdZ2E2np5QEnYfL
},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-32606-6_22},
year = {2023},
date = {2023-05-27},
urldate = {2023-05-27},
booktitle = {International Conference on Robotics in Alpe-Adria-Danube Region (RAAD). },
volume = {135},
pages = {186 - 194},
publisher = {Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland.},
series = {Mechanisms and Machine Science},
abstract = {Simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) algorithms are essential for the autonomous navigation of mobile robots. With the increasing demand for autonomous systems, it is crucial to evaluate and compare the performance of these algorithms in real-world environments.
In this paper, we provide an evaluation strategy and real-world datasets to test and evaluate SLAM algorithms in complex and challenging indoor environments. Further, we analysed state-of-the-art (SOTA) SLAM algorithms based on various metrics such as absolute trajectory error, scale drift, and map accuracy and consistency. Our results demonstrate that SOTA SLAM algorithms often fail in challenging environments, with dynamic objects, transparent and reflecting surfaces. We also found that successful loop closures had a significant impact on the algorithm’s performance. These findings highlight the need for further research to improve the robustness of the algorithms in real-world scenarios. },
keywords = {mobile navigation, robotics, SLAM},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
Simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) algorithms are essential for the autonomous navigation of mobile robots. With the increasing demand for autonomous systems, it is crucial to evaluate and compare the performance of these algorithms in real-world environments.
In this paper, we provide an evaluation strategy and real-world datasets to test and evaluate SLAM algorithms in complex and challenging indoor environments. Further, we analysed state-of-the-art (SOTA) SLAM algorithms based on various metrics such as absolute trajectory error, scale drift, and map accuracy and consistency. Our results demonstrate that SOTA SLAM algorithms often fail in challenging environments, with dynamic objects, transparent and reflecting surfaces. We also found that successful loop closures had a significant impact on the algorithm’s performance. These findings highlight the need for further research to improve the robustness of the algorithms in real-world scenarios. | 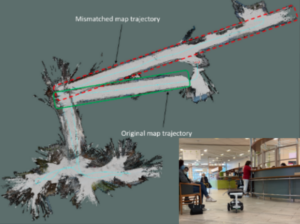 |

