2024
|
Lygerakis, Fotios; Dave, Vedant; Rueckert, Elmar M2CURL: Sample-Efficient Multimodal Reinforcement Learning via Self-Supervised Representation Learning for Robotic Manipulation Proceedings Article In: IEEE International Conference on Ubiquitous Robots (UR 2024), IEEE 2024. @inproceedings{Lygerakis2024,
title = {M2CURL: Sample-Efficient Multimodal Reinforcement Learning via Self-Supervised Representation Learning for Robotic Manipulation},
author = {Fotios Lygerakis and Vedant Dave and Elmar Rueckert},
url = {https://cloud.cps.unileoben.ac.at/index.php/s/NPejb2Fp4Y8LeyZ},
year = {2024},
date = {2024-04-04},
urldate = {2024-04-04},
booktitle = {IEEE International Conference on Ubiquitous Robots (UR 2024)},
organization = {IEEE},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
| 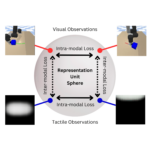 |
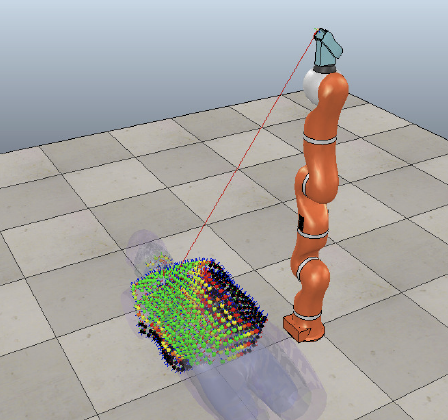
Dave*, Vedant; Lygerakis*, Fotios; Rueckert, Elmar Multimodal Visual-Tactile Representation Learning through Self-Supervised Contrastive Pre-Training Proceedings Article In: IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 8013-8020, IEEE, 2024, ISBN: 979-8-3503-8457-4, (* equal contribution). @inproceedings{Dave2024b,
title = {Multimodal Visual-Tactile Representation Learning through Self-Supervised Contrastive Pre-Training},
author = {Vedant Dave* and Fotios Lygerakis* and Elmar Rueckert},
url = {https://cloud.cps.unileoben.ac.at/index.php/s/Nw9TprfdDoLgr8e},
doi = {10.1109/ICRA57147.2024.10610228},
isbn = {979-8-3503-8457-4},
year = {2024},
date = {2024-01-28},
urldate = {2024-01-28},
booktitle = {IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA)},
pages = {8013-8020},
publisher = {IEEE},
abstract = {The rapidly evolving field of robotics necessitates methods that can facilitate the fusion of multiple modalities. Specifically, when it comes to interacting with tangible objects, effectively combining visual and tactile sensory data is key to understanding and navigating the complex dynamics of the physical world, enabling a more nuanced and adaptable response to changing environments. Nevertheless, much of the earlier work in merging these two sensory modalities has relied on supervised methods utilizing datasets labeled by humans. This paper introduces MViTac, a novel methodology that leverages contrastive learning to integrate vision and touch sensations in a self-supervised fashion. By availing both sensory inputs, MViTac leverages intra and inter-modality losses for learning representations, resulting in enhanced material property classification and more adept grasping prediction. Through a series of experiments, we showcase the effectiveness of our method and its superiority over existing state-of-the-art self-supervised and supervised techniques. In evaluating our methodology, we focus on two distinct tasks: material classification and grasping success prediction. Our results indicate that MViTac facilitates the development of improved modality encoders, yielding more robust representations as evidenced by linear probing assessments. https://sites.google.com/view/mvitac/home},
note = {* equal contribution},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
The rapidly evolving field of robotics necessitates methods that can facilitate the fusion of multiple modalities. Specifically, when it comes to interacting with tangible objects, effectively combining visual and tactile sensory data is key to understanding and navigating the complex dynamics of the physical world, enabling a more nuanced and adaptable response to changing environments. Nevertheless, much of the earlier work in merging these two sensory modalities has relied on supervised methods utilizing datasets labeled by humans. This paper introduces MViTac, a novel methodology that leverages contrastive learning to integrate vision and touch sensations in a self-supervised fashion. By availing both sensory inputs, MViTac leverages intra and inter-modality losses for learning representations, resulting in enhanced material property classification and more adept grasping prediction. Through a series of experiments, we showcase the effectiveness of our method and its superiority over existing state-of-the-art self-supervised and supervised techniques. In evaluating our methodology, we focus on two distinct tasks: material classification and grasping success prediction. Our results indicate that MViTac facilitates the development of improved modality encoders, yielding more robust representations as evidenced by linear probing assessments. https://sites.google.com/view/mvitac/home | 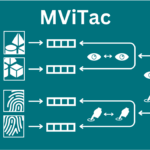 |
2023
|
Lygerakis, Fotios; Rueckert, Elmar CR-VAE: Contrastive Regularization on Variational Autoencoders for Preventing Posterior Collapse Proceedings Article In: Asian Conference of Artificial Intelligence Technology (ACAIT)., IEEE, 2023. @inproceedings{Lygerakis2023,
title = {CR-VAE: Contrastive Regularization on Variational Autoencoders for Preventing Posterior Collapse},
author = {Fotios Lygerakis and Elmar Rueckert},
url = {https://cloud.cps.unileoben.ac.at/index.php/s/fNNRnzJFPrtGQM2},
year = {2023},
date = {2023-08-16},
urldate = {2023-08-16},
booktitle = {Asian Conference of Artificial Intelligence Technology (ACAIT).},
publisher = {IEEE},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
|  |
2021
|
Lygerakis, Fotios; Dagioglou, Maria; Karkaletsis, Vangelis Accelerating Human-Agent Collaborative Reinforcement Learning Conference In Proceedings of the 14th PErvasive Technologies Related to Assistive Environments Conference (PETRA '21), Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, 90–92, 2021. @conference{nokey,
title = {Accelerating Human-Agent Collaborative Reinforcement Learning},
author = {Fotios Lygerakis and Maria Dagioglou and Vangelis Karkaletsis},
url = {https://cps.unileoben.ac.at/3453892-3454004/},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1145/3453892.3454004},
year = {2021},
date = {2021-06-29},
urldate = {2021-06-29},
booktitle = {In Proceedings of the 14th PErvasive Technologies Related to Assistive Environments Conference (PETRA '21)},
pages = {90-92},
publisher = {Association for Computing Machinery},
address = {New York, NY, USA, 90–92},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {conference}
}
|  |
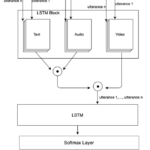
Banerjee, Debapriya; Lygerakis, Fotios; Makedon, Fillia Sequential Late Fusion Technique for Multi-modal Sentiment Analysis Conference In Proceedings of the 14th PErvasive Technologies Related to Assistive Environments Conference (PETRA '21), Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, 264–265. , 2021. @conference{nokey,
title = {Sequential Late Fusion Technique for Multi-modal Sentiment Analysis},
author = {Debapriya Banerjee and Fotios Lygerakis and Fillia Makedon},
url = {https://cps.unileoben.ac.at/3453892-34610091/},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1145/3453892.3461009},
year = {2021},
date = {2021-06-29},
urldate = {2021-06-29},
booktitle = {In Proceedings of the 14th PErvasive Technologies Related to Assistive Environments Conference (PETRA '21)},
journal = {In Proceedings of the 14th PErvasive Technologies Related to Assistive Environments Conference (PETRA '21)},
publisher = {Association for Computing Machinery},
address = {New York, NY, USA, 264–265. },
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {conference}
}
|  |
Kyrarini, Maria; Lygerakis, Fotios; Rajavenkatanarayanan, Akilesh; Sevastopoulos, Christos; Nambiappan, Harish Ram; Chaitanya, Kodur Krishna; Babu, Ashwin Ramesh; Mathew, Joanne; Makedon, Fillia A Survey of Robots in Healthcare Journal Article In: Technologies, vol. 9, iss. 8, 2021. @article{nokey,
title = { A Survey of Robots in Healthcare },
author = {Maria Kyrarini and Fotios Lygerakis and Akilesh Rajavenkatanarayanan and Christos Sevastopoulos and Harish Ram Nambiappan and Kodur Krishna Chaitanya and Ashwin Ramesh Babu and Joanne Mathew and Fillia Makedon},
url = {https://cps.unileoben.ac.at/technologies-09-00008/},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies9010008 },
year = {2021},
date = {2021-01-18},
urldate = {2021-01-18},
journal = { Technologies},
volume = {9},
issue = {8},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|  |
2020
|
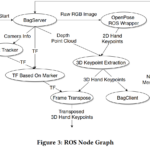
Lygerakis, Fotios; Tsitos, Athanasios C; Dagioglou, Maria; Makedon, Fillia; Karkaletsis, Vangelis Evaluation of 3D markerless pose estimation accuracy using openpose and depth information from a single RGB-D camera Conference In Proceedings of the 13th ACM International Conference on PErvasive Technologies Related to Assistive Environments (PETRA '20), Article 75, 1–6 Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, 2020. @conference{nokey,
title = {Evaluation of 3D markerless pose estimation accuracy using openpose and depth information from a single RGB-D camera},
author = {Fotios Lygerakis and Athanasios C Tsitos and Maria Dagioglou and Fillia Makedon and Vangelis Karkaletsis},
url = {https://cps.unileoben.ac.at/petra_20___evaluation__of__3d__markerless__pose_estimation__accuracy__using__openpose_and_depth_information_from_a_single_rgb_d_camera/},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1145/3389189.3398005},
year = {2020},
date = {2020-06-30},
booktitle = {In Proceedings of the 13th ACM International Conference on PErvasive Technologies Related to Assistive Environments (PETRA '20)},
publisher = {Association for Computing Machinery},
address = {New York, NY, USA},
series = {Article 75, 1–6},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {conference}
}
|  |
Diakoloukas, Vassilios; Lygerakis, Fotios; Lagoudakis, Michail G; Kotti, Margarita Variational Denoising Autoencoders and Least-Squares Policy Iteration for Statistical Dialogue Manager Journal Article In: IEEE Signal Processing Letters , vol. 27, pp. 960-964, 2020. @article{nokey,
title = {Variational Denoising Autoencoders and Least-Squares Policy Iteration for Statistical Dialogue Manager},
author = {Vassilios Diakoloukas and Fotios Lygerakis and Michail G Lagoudakis and Margarita Kotti},
url = {https://cps.unileoben.ac.at/sigprocletters2020_kotti/},
doi = {10.1109/LSP.2020.2998361.},
year = {2020},
date = {2020-05-28},
urldate = {2020-05-28},
journal = {IEEE Signal Processing Letters },
volume = {27},
pages = {960-964},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|  |
2019
|
Lygerakis, Fotios; Diakoloulas, Vassilios; Lagoudakis, Michail; Kotti, Margarita Robust Belief State Space Representation for Statistical Dialogue Managers Using Deep Autoencoders Conference 2019 IEEE Automatic Speech Recognition and Understanding Workshop (ASRU), 2019. @conference{nokey,
title = {Robust Belief State Space Representation for Statistical Dialogue Managers Using Deep Autoencoders},
author = {Fotios Lygerakis and Vassilios Diakoloulas and Michail Lagoudakis and Margarita Kotti},
url = {https://cps.unileoben.ac.at/asru2019_robust_belief_state_space_representation/},
doi = {10.1109/ASRU46091.2019.9003871.},
year = {2019},
date = {2019-12-14},
urldate = {2020-02-20},
booktitle = {2019 IEEE Automatic Speech Recognition and Understanding Workshop (ASRU)},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {conference}
}
|  |