Course Content
In the first week, advanced machine and deep learning methods like multi-layer-perceptrons, convolutional neural networks, variational autoencoder, transformers, simultaneous navigation and mapping approaches, and more will be presented.
These methods can be tested using interactive tools like for example using https://playground.tensorflow.org. To deepen the knowledge, students will answer well-crafted scientific questions using latex handouts alone or in teams of two students in the lecture room.
Additionally, Jupyter notebook files were prepared to implement advanced machine and deep learning approaches without installing any software. For all participants of the course user accounts will be created using our JupyterHub at https://jupyter.cps.unileoben.ac.at. The accounts will remain active till the end of the semester.
Prerequisites & If you Miss Course Contents
During the first week, a laptop or tablet will be needed to use the interactive tools and the Jupyter notebooks.
When you miss some course contens
If you miss some course contents due to overlapping events, you can watch recordings of the sessions online. All recordings will be hosted via Moodle at https://moodle.unileoben.ac.at/course/view.php?id=3082.
Course Description
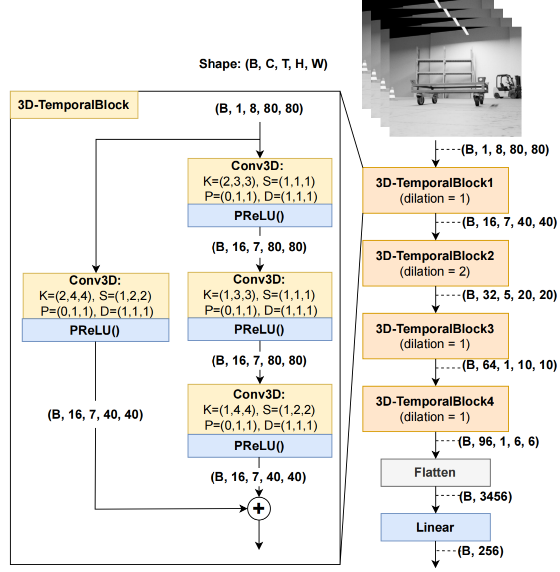
Modern machine learning methods and in particular deep learning methods are entering almost all areas of engineering.
The integrated course enables the students to apply these methods in the application domains of their study.
For this purpose, current problems from the industry are investigated and the possibilities of machine and deep learning methods are tested.
Students gain a deep understanding of method implementations, how data must be prepared, which criteria are relevant for selecting learning methods, and how evaluations must be performed in order to interpret the results in a meaningful way.
Initially, the basics of learning methods are developed in 5-6 lecture units. Then, students select one of the listed industrial problems and work on it alone or as a team (with extended assignments). The project work is accompanied by weekly tutorials with tips and tricks. Finally, the project results are discussed in a written report and presented for a final 10-15min.
Grading is based on the quality of the code, the report, and the final short presentation.
Among others, one of the following industry problems can be chosen:
1. Application and comparison of deep neural networks for steel quality prediction in continuous casting plants with data from the ‘Stahl- und Walzwerk Marienhütte GmbH Graz’.
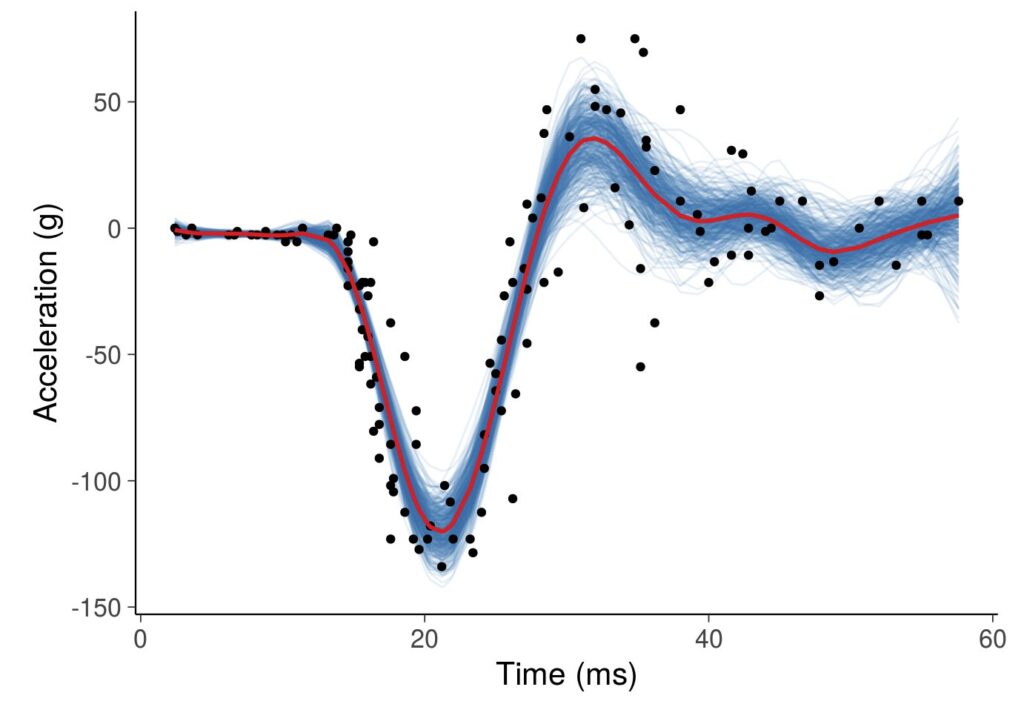
2. Predictive maintenance of bearing shells using frequency analysis in decision trees and deep neural networks based on acoustic measurement data.
3. Motion analysis and path planning for human-machine interaction in logistics tasks with mobile robots of the Chair of CPS.
4. Autonomous navigation and mapping with RGB-D cameras of the four-legged robot Unitree Go1 for excavation inspection in mining.
The project list is continuously extended.
Links and Resources
Location & Time
- Location: HS 3 Studienzentrum
- Dates: 01.10.2024 – 07.10.2024, see the course schedule above.
- Location: Digital Science Center (Roseggerstraße 11, 8700 Leoben)
- Date: 22.01.2025, 10:15 – 15:15, final presentation
Kickoff meeting of project
All meetings will be conducted at CPS chair. The time please refer to the email, contact us if reschedule is needed.
Previous Knowledge Expected
Formal Prerequisite: Basic Python programming skills, Fundamentals of Statistics.
Recommended Prerequisites: Introduction to Machine Learning (“190.012” and “190.013”).
Slides
- 01.10.2024
- 02.10.2024
- 03.10.2024
- 04.10.2024
- 22.01.2024
Learning objectives / qualifications
- Implement or independently adapt modern machine learning methods and in particular deep learning methods in Python.
- Analyze data of complex industrial problems, process (filter) the data, and divide it into training- and test data sets such that a meaningful interpretation is possible.
- Define criteria and metrics to evaluate evaluations and predictions and generate statistics.
- Develop, evaluate, and discuss meaningful experiments and evaluations.
- Identify and describe assumptions, problems, and ideas for improvement of practical learning problems.
Grading
Continuous assessment: During the lectures and the tutorials 0-20 bonus points can be collected through active participation.
Project assignments: Alone or in small groups (2-3 students) one of the listed projects has to be implemented. A written report in form of a git repository wiki page have to be submitted.
– For the implementation (Python Code) 0-40 Points can be obtained.
– For the wiki page report, 0-60 Points will be given.
Grading scheme: 0-49,9 Points (5), 50-65,9 Points (4), 66-79 Points (3), 80-91 Points (2), 92-100 Points (1).
With an overall score of up to 79%, an additional oral performance review MAY (!) also be required if the positive performance record is not clear. In this case, you will be informed as soon as the grades are released. If you have already received a grade via MU online, you will not be invited to another oral performance review.
Literature
Machine Learning and Data-modelling:
– Rueckert Elmar 2022. An Introduction to Probabilistic Machine Learning, https://cloud.cps.unileoben.ac.at/index.php/s/iDztK2ByLCLxWZA
– James-A. Goulet 2020. Probabilistic Machine Learning for Civil Engineers. MIT Press.
– Bishop 2006. Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning, Springer.
Learning method Programming in Python:
– Sebastian Raschka, YuxiH. Liu and Vahid Mirjalili 2022. Machine Learning with PyTorch and Scikit- Learn. Packt Publishing Ltd, UK.
– Matthieu Deru and Alassane Ndiaye 2020. Deep Learning mit TensorFlow, Keras und TensorFlow.js., Rheinwerk-verlag, DE.
Problem specific Literature:
– B. Siciliano, L.Sciavicco 2009. Robotics: Modelling, Planning and Control, Springer.
– Kevin M. Lynch and FrankC. Park 2017. MODERN ROBOTICS, MECHANICS, PLANNING, AND CONTROL, Cambridge University Press.
– E.T. Turkogan 1996. Fundamentals of Steelmaking. Maney Publishing,UK.