2025
|
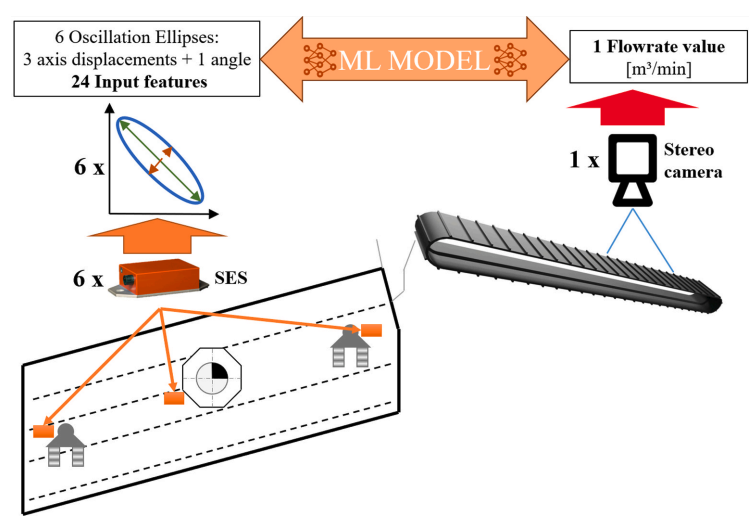
Krukenfellner, Philip; Rueckert, Elmar; Flachberger, Helmut Prediction of feed flowrates, based on vibration patterns, generated by vibration sensors on an industrial circular vibrating screen using a set of ML models Journal Article In: Minerals Engineering, vol. 237, 2025. @article{Krukenfellner2025,
title = {Prediction of feed flowrates, based on vibration patterns, generated by vibration sensors on an industrial circular vibrating screen using a set of ML models},
author = {Philip Krukenfellner and Elmar Rueckert and Helmut Flachberger},
url = {https://cloud.cps.unileoben.ac.at/index.php/s/tee9587mMEnX3Aw
},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2025.109963},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-11-21},
urldate = {2025-11-21},
journal = {Minerals Engineering},
volume = {237},
keywords = {Applied Deep Learning},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|  |
Keshavarz, Sahar; Elmgerbi, Asad; Dave, Vedant; Rückert, Elmar; Thonhauser, Gerhard Deep reinforcement learning for automated decision-making in wellbore construction Journal Article In: Energy Reports, vol. 14, pp. 3514-3528, 2025, ISSN: 2352-4847. @article{KESHAVARZ20253514,
title = {Deep reinforcement learning for automated decision-making in wellbore construction},
author = {Sahar Keshavarz and Asad Elmgerbi and Vedant Dave and Elmar Rückert and Gerhard Thonhauser},
url = {https://cloud.cps.unileoben.ac.at/index.php/s/X9wYbSpemJqrkW8},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egyr.2025.10.028},
issn = {2352-4847},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-11-02},
urldate = {2025-11-02},
journal = {Energy Reports},
volume = {14},
pages = {3514-3528},
abstract = {The drilling industry continuously seeks cost reduction through improved efficiency, with automation seen as a key solution. The drilling industry continuously seeks cost reduction through improved efficiency, with automation viewed as a key enabler. However, due to the complexity of drilling operations, uncertainty in subsurface conditions, and limitations in real-time data, achieving reliable autonomy remains a major challenge. While physics-based models support automation, they often face limitations under real-time constraints and may struggle to adapt effectively in the presence of uncertain or incomplete data. This study contributes to automation efforts by employing Reinforcement Learning (RL) to model hole conditioning, an essential part of drilling operation. Using a Q-learning approach, the RL agent optimizes operational decisions in real time, adapting based on environmental feedback. This artificial intelligence (AI) -driven agent identifies the ideal sequence of actions for circulation, reaming, and washing, maximizing operational safety and efficiency by aligning with target parameters while navigating operational constraints. The RL model decisions were benchmarked against real-case actions, demonstrating that the agent strategy can outperform expert choices in several areas. Specifically, the RL model provided better solutions in three key examples: avoiding poor hole cleaning, lowering the operational time, and preventing wellbore stability issues. The proposed system contributes to the growing body of research applying deep reinforcement learning for automated hole conditioning, representing an innovative engineering application for AI. This approach not only enhances real-time decision-making capabilities but also establishes a foundation for further automation in well construction, integrating engineering requirements with advanced AI-driven strategies. Through the combination of AI and practical engineering design, this work advances both automation and safety in drilling operations, signaling a promising step forward for future developments in wellbore construction.},
keywords = {Applied Deep Learning, Reinforcement Learning},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
The drilling industry continuously seeks cost reduction through improved efficiency, with automation seen as a key solution. The drilling industry continuously seeks cost reduction through improved efficiency, with automation viewed as a key enabler. However, due to the complexity of drilling operations, uncertainty in subsurface conditions, and limitations in real-time data, achieving reliable autonomy remains a major challenge. While physics-based models support automation, they often face limitations under real-time constraints and may struggle to adapt effectively in the presence of uncertain or incomplete data. This study contributes to automation efforts by employing Reinforcement Learning (RL) to model hole conditioning, an essential part of drilling operation. Using a Q-learning approach, the RL agent optimizes operational decisions in real time, adapting based on environmental feedback. This artificial intelligence (AI) -driven agent identifies the ideal sequence of actions for circulation, reaming, and washing, maximizing operational safety and efficiency by aligning with target parameters while navigating operational constraints. The RL model decisions were benchmarked against real-case actions, demonstrating that the agent strategy can outperform expert choices in several areas. Specifically, the RL model provided better solutions in three key examples: avoiding poor hole cleaning, lowering the operational time, and preventing wellbore stability issues. The proposed system contributes to the growing body of research applying deep reinforcement learning for automated hole conditioning, representing an innovative engineering application for AI. This approach not only enhances real-time decision-making capabilities but also establishes a foundation for further automation in well construction, integrating engineering requirements with advanced AI-driven strategies. Through the combination of AI and practical engineering design, this work advances both automation and safety in drilling operations, signaling a promising step forward for future developments in wellbore construction. | 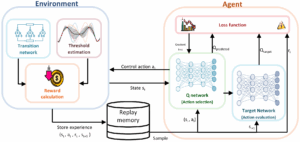 |
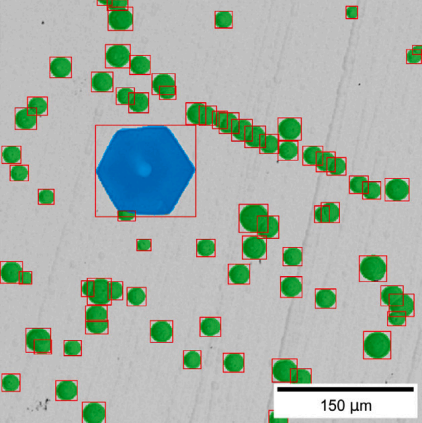
Holub, Georg; Hofer, Sebastian; Obermüller, Thomas; Rueckert, Elmar; Romaner, Lorenz Instance segmentation pipeline for etch pit detection and prismatic slip characterization on silicon carbide substrates Journal Article In: Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, vol. 160, 2025, ISBN: 0952-1976. @article{Holub2025,
title = {Instance segmentation pipeline for etch pit detection and prismatic slip characterization on silicon carbide substrates},
author = {Georg Holub and Sebastian Hofer and Thomas Obermüller and Elmar Rueckert and Lorenz Romaner},
url = {https://cloud.cps.unileoben.ac.at/index.php/s/SqcW9EttRzo3GwB},
isbn = {0952-1976},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-08-12},
urldate = {2025-08-12},
journal = {Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence},
volume = {160},
keywords = {Applied Deep Learning, Material Science},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|  |
Trimmel, Simone; Spörl, Philipp; Haluza, Daniela; Meisel, Thomas C; Pitha, Ulrike; Prohaska, Thomas; Puschenreiter, Markus; Rueckert, Elmar; Spangl, Bernhard; Wiedenhofer, Dominik; Irrgeher, Johanna Determination of Technology-Critical Elements in Urban Plants and Water using Inductively Coupled Plasma Tandem Mass Spectrometry Conference SETAC Europe 35th Annual Meeting, 2025, (Extended Abstract). @conference{Trimmel2025,
title = {Determination of Technology-Critical Elements in Urban Plants and Water using Inductively Coupled Plasma Tandem Mass Spectrometry},
author = {Simone Trimmel and Philipp Spörl and Daniela Haluza and Thomas C Meisel and Ulrike Pitha and Thomas Prohaska and Markus Puschenreiter and Elmar Rueckert and Bernhard Spangl and Dominik Wiedenhofer and Johanna Irrgeher},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-05-13},
urldate = {2025-05-13},
booktitle = {SETAC Europe 35th Annual Meeting},
note = {Extended Abstract},
keywords = {Applied Deep Learning},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {conference}
}
| |
Koinig, Gerald; Neubauer, Melanie; Martinelli, Walter; Radmann, Yves; Kuhn, Nikolai; Fink, Thomas; Rueckert, Elmar; Tischberger-Aldrian, Alexia CNN-based copper reduction in shredded scrap for enhanced electric arc furnace steelmaking Proceedings Article In: International Conference on Optical Characterization of Materials (OCM 2025), pp. 319-328, 2025, ISBN: 9783731514084. @inproceedings{nokey,
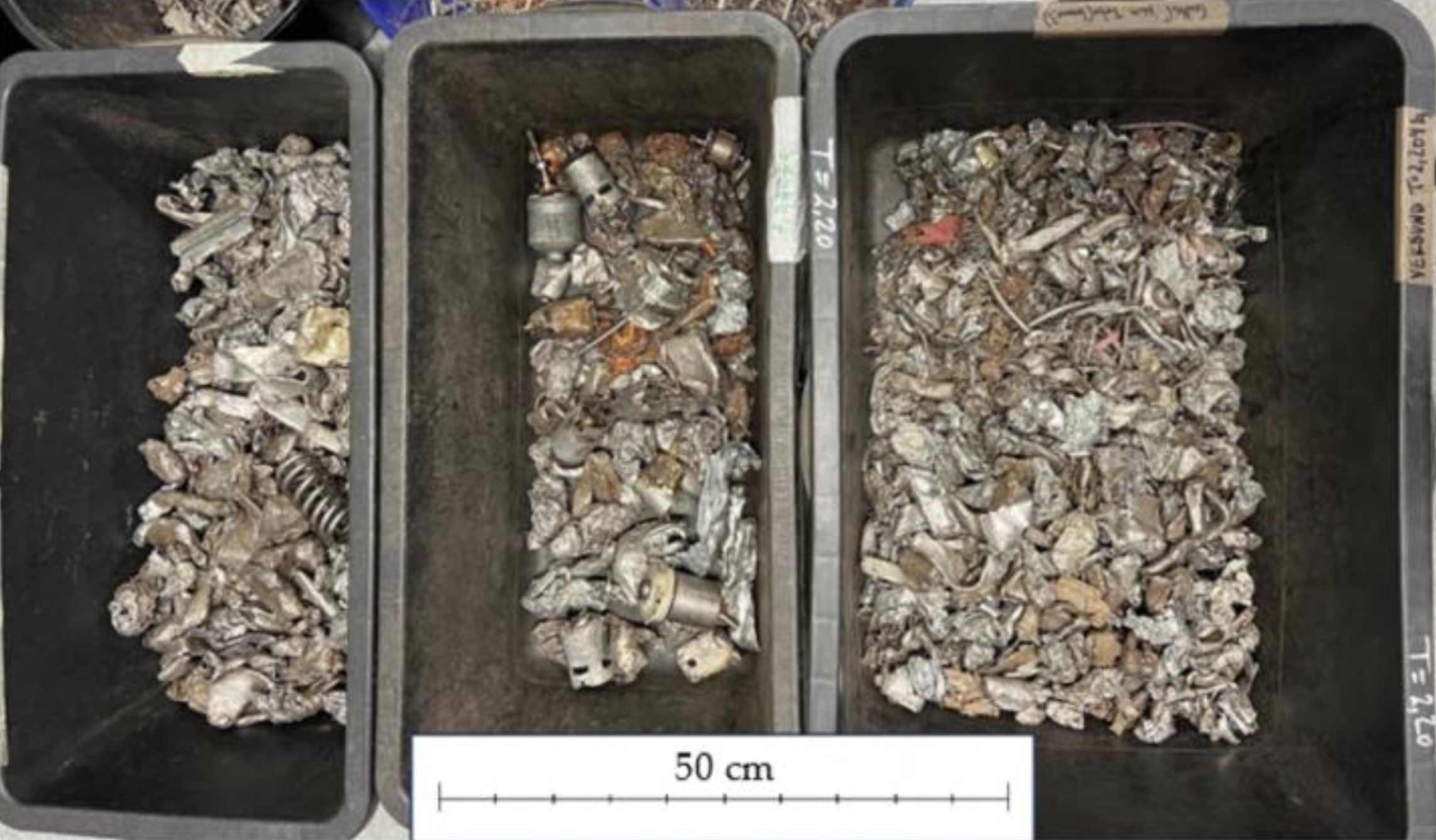
title = {CNN-based copper reduction in shredded scrap for enhanced electric arc furnace steelmaking},
author = {Gerald Koinig and Melanie Neubauer and Walter Martinelli and Yves Radmann and Nikolai Kuhn and Thomas Fink and Elmar Rueckert and Alexia Tischberger-Aldrian},
url = {http://www.scopus.com/inward/record.url?scp=105005090678&partnerID=8YFLogxK
https://books.google.de/books?hl=de&lr=&id=cQtZEQAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PA329&dq=CNN-based+copper+reduction+in+shredded+scrap+for+enhanced+electric+arc+furnace+steelmaking&ots=UK8_ZX8DWo&sig=9itL3MMW7ZDb1HK5rucwcYwVzG0
},
isbn = {9783731514084},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-03-26},
urldate = {2025-03-26},
booktitle = {International Conference on Optical Characterization of Materials (OCM 2025)},
pages = {319-328},
keywords = {Applied Deep Learning, neural network, Recycling},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
|  |
2024
|
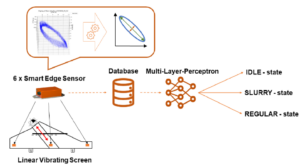
Krukenfellner, Philip; Rueckert, Elmar; Flachberger, Helmut Predicting condition states, based on displacement data, generated by acceleration sensors on industrial linear vibrating screens through neural networks Journal Article In: IEEE Sensors Journal, pp. 1–13, 2024, ISBN: 1558-1748. @article{Krukenfellner2024,
title = {Predicting condition states, based on displacement data, generated by acceleration sensors on industrial linear vibrating screens through neural networks},
author = {Philip Krukenfellner and Elmar Rueckert and Helmut Flachberger},
url = {https://cloud.cps.unileoben.ac.at/index.php/s/GJN9XCBzW5TqPys},
isbn = {1558-1748},
year = {2024},
date = {2024-10-04},
urldate = {2024-10-04},
journal = {IEEE Sensors Journal},
pages = {1--13},
keywords = {Applied Deep Learning, Industrial Applications, Vibrating Screens},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|  |
Trimmel, Simone; Spörl, Philipp; Haluza, Daniela; Lashin, Nagi; Meisel, Thomas C.; Pitha, Ulrike; Prohaska, Thomas; Puschenreiter, Markus; Rückert, Elmar; Spangl, Bernhard; Wiedenhofer, Dominik; Irrgeher, Johanna Green and blue infrastructure as model system for emissions of technology-critical elements Journal Article In: Science of The Total Environment, vol. 934, 2024, ISBN: 0048-9697, (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.173364). @article{Trimmel2024,
title = {Green and blue infrastructure as model system for emissions of technology-critical elements},
author = {Simone Trimmel and Philipp Spörl and Daniela Haluza and Nagi Lashin and Thomas C. Meisel and Ulrike Pitha and Thomas Prohaska and Markus Puschenreiter and Elmar Rückert and Bernhard Spangl and Dominik Wiedenhofer and Johanna Irrgeher},
url = {https://cloud.cps.unileoben.ac.at/index.php/s/WJwtk2JC4XnyzL6},
isbn = {0048-9697},
year = {2024},
date = {2024-05-21},
journal = {Science of The Total Environment},
volume = {934},
note = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.173364},
keywords = {Applied Deep Learning, environmental health risks, pollution},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|  |





